All you need to know about collagen
-
 GOLD COLLAGEN
GOLD COLLAGEN - Nutrition And Beauty
- January 12, 2018
Without a doubt you would have read about or even used collagen-based supplements. Collagen has been trending for quite some time because it is a key factor in supporting our skin, hair and nail health. Collagen is readily available in nearly any form including liquid, powder, tablets, capsules and even as chewy gummies.
What exactly is collagen?
Collagen is the main structural protein of different connective tissues that holds the body together. For the skin, collagen acts as scaffolding helping to strengthen and structure it to look plump and healthy. Collagen is rich in amino acids, so when it comes to joints and tendons it plays an important role in building cartilage. It also has anti-inflammatory properties.
How is collagen produced?
Collagen is produced by fibroblasts and chondrocytes, which are cells in the connective tissues of the body. However certain types of collagen can also be made by numerous epithelial cells. Epithelial cells line the surface of your body and internal organs.
Where is collagen found?
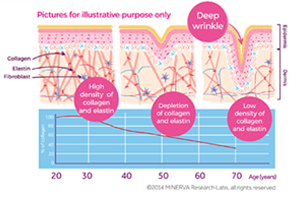
Collagen is mostly found in fibrous tissues, such as tendons and ligaments. You can find generous amounts of collagen in the cornea, cartilage, bones, blood vessels, the gut and intervertebral discs. When it comes to our skin, collagen is the major insoluble fibrous protein along with elastin and hyaluronic acid and is found in the extracellular matrix of the skin.
Unfortunately, once we reach the age of 25 the body’s own ability to produce collagen rapidly decreases. Therefore, our skin will begin to lose its firmness and wrinkles will start to appear. Food such as animal cartilage or poultry skin may provide collagen, however not everyone would be comfortable eating those. Further, those foods do not contain as much collagen as the body requires to keep skin supple and joints healthy.
In order to understand how to best support your body and wellbeing by taking collagen, we will next explain the different types of collagen and their specific benefits.
Dr. Sara Sibilla